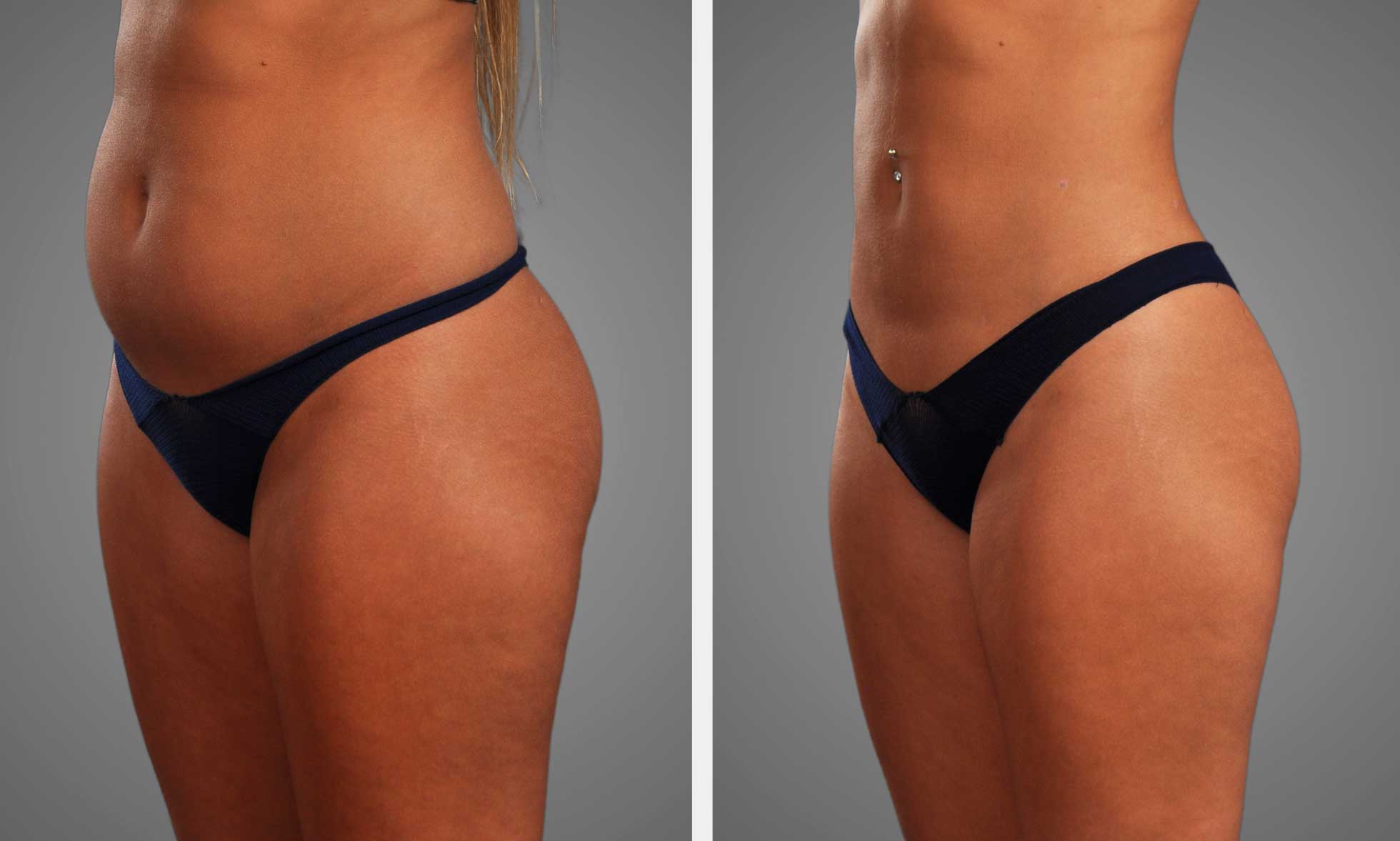
Fat transfer grafting has emerged as a revolutionary technique in the realm of cosmetic and reconstructive surgery, offering a dual benefit by removing unwanted fat from one area of the body and using it to enhance another. This procedure not only promises a more natural look compared to synthetic fillers but also boasts a lower risk of allergic reactions, making it an increasingly popular choice among patients seeking aesthetic improvements or reconstructive solutions. As we delve into the intricacies of fat transfer grafting, we’ll explore its advantages, process, and potential outcomes for those considering this cutting-edge treatment option.
Understanding Fat Transfer Breast Augmentation
Natural Enhancement
Fat transfer breast augmentation offers a natural alternative to traditional implants. This procedure utilizes the patient’s own fat, harvested from other body parts through liposuction. It is an appealing option for those seeking subtle enhancements without synthetic materials.
The process begins with identifying donor sites, areas with excess fat like the abdomen or thighs. The extracted fat is then purified and prepared for injection into the breasts. This method not only enhances breast size but also improves body contour by removing unwanted fat deposits.
Procedure Steps
-
Consultation: The first step involves discussing goals and evaluating suitability.
-
Harvesting: Fat is removed from selected areas using liposuction.
-
Purification: Extracted fat undergoes purification to prepare it for grafting.
-
Injection: Purified fat cells are carefully injected into the breasts.
This approach ensures a more natural look and feel compared to silicone or saline implants. Recovery time varies but generally includes some swelling and bruising at both the extraction and injection sites.
Pros of this method include:
-
Utilization of one’s own tissue reduces rejection risks.
-
Dual benefit of reducing unwanted fat while enhancing breast volume.
-
Absence of implant-related complications such as rupture or displacement.
However, limitations exist:
-
Not suitable for those desiring significant size increase.
-
Potential for some reabsorbed fat leading to asymmetry or need for additional procedures.
Exploring Breast Augmentation Techniques
Fat Transfer Grafting
Fat transfer grafting involves moving fat from one body part to another. This method is less invasive than implant surgery. It uses a patient’s own body fat, reducing the risk of rejection.
The procedure starts with liposuction, removing excess fat. Then, it’s processed and injected into the breasts. Recovery time is generally shorter compared to implants. However, the increase in breast size may be more subtle.
Implant Options
Breast implants come in two main types: silicone and saline. Silicone implants are filled with silicone gel, while saline implants contain sterile salt water.
Silicone offers a more natural feel but requires regular breast imaging checks for leaks. Saline implants provide a firmer feel and any leakage is safely absorbed by the body. Both require surgical insertion and have longer recovery periods than fat transfer grafting.
Suitability Considerations
Choosing between these methods depends on several factors:
-
Desired outcome
-
Body type
-
Health considerations
-
Personal preference
For significant enlargement, implants might be preferable. Fat transfer suits those seeking modest increases or more natural results. Consultation with a certified plastic surgeon is crucial for making an informed decision.
Determining Suitability for Fat Transfer Breast Augmentation
Donor Fat Necessity
Fat transfer breast augmentation relies heavily on the patient’s adipose tissue. Not everyone has enough donor fat for this procedure. The need for sufficient donor fat cannot be overstated. Without it, achieving desired results is impossible.
Patients must have enough body fat in other areas to harvest. Common areas include the abdomen, thighs, and buttocks. If a patient lacks adequate adipose tissue, alternatives may need consideration.

Health and Structure
Overall health plays a crucial role in determining suitability. Patients should be healthy with no underlying conditions that could impair healing or affect outcomes.
Breast structure also matters significantly. The quality of the existing breast tissue can influence both the potential for success and the aesthetic outcome of fat transfer grafting.
Expectation Management
Managing expectations is key in fat transfer breast augmentation decisions.
-
Desired size increase might not always be achievable.
-
Shape improvements are possible but vary among patients.
It’s important to have realistic expectations about what can be achieved through this procedure:
-
Size increases are generally modest.
-
Shape enhancements depend on individual anatomy and amount of available adipose tissue.
Understanding these limitations helps set realistic goals and satisfaction with results.
Evaluating Risks of Fat Transfer to Breasts
Common Complications
After determining suitability for fat transfer breast augmentation, it’s crucial to consider the potential risks involved. Swelling and bruising are common after the procedure. These issues usually resolve within a few weeks but can cause discomfort.
Another concern is asymmetry, where one breast may appear different in size or shape compared to the other. This can happen if fat cells do not survive evenly in both breasts.
Long-Term Risks
One notable long-term risk is the formation of oil cysts. These occur when transferred fat cells die and release their contents, forming lumps that can sometimes be felt under the skin.
There’s a potential impact on mammogram readings. The presence of oil cysts or scar tissue from the procedure might make mammograms harder to read. This could potentially obscure detection of cancerous changes.
Identifying Risks of Fat Necrosis in Breast Augmentation
Fat Necrosis Defined
Fat necrosis occurs when fatty tissue inside the breast gets damaged. This can lead to lumps, pain, and skin changes. These symptoms might alarm patients as they resemble those of more serious conditions.
The appearance of fat necrosis varies. Some may notice a firm lump under their skin or experience tenderness in the area. Skin over the affected area could also appear reddish or bruised.
Impact on Appearance
Fat necrosis can alter the look of breasts post-augmentation. Lumps formed by damaged tissue might create an uneven surface or distort the shape of the breast.
In most cases, these cosmetic issues are minor and resolve with time. However, some instances require corrective surgery to restore symmetry and achieve desired results.
Surgical Correction
Corrective surgery for fat necrosis is rare but necessary in certain situations. If lumps persist or cause discomfort, surgical intervention becomes an option.
-
Pros:
-
Removes painful lumps.
-
Restores breast symmetry.
-
Cons:
-
Additional recovery time.
-
Possible complications from another procedure.
Most patients never need this step thanks to modern techniques that minimize complications during fat transfer grafting.
Identifying risks early helps manage expectations and prepare for possible outcomes after breast augmentation using fat transfer grafting. Although major complications like significant fat necrosis requiring surgery are uncommon, being aware allows for prompt action if needed.
Assessing Risk of Infection in Fat Transfer Breast Augmentation
Infection Signs
After undergoing fat transfer breast augmentation, patients should be vigilant for signs of infection. These signs include redness, fever, and unusual discharge around the surgical area. Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial for prompt treatment.
Infections can escalate if not treated timely. It’s essential to contact a healthcare provider immediately upon noticing any concerning signs. They will guide you through the necessary steps to manage the situation effectively.
Choosing Surgeons
The choice of surgeon plays a pivotal role in minimizing infection risks during fat transfer grafting procedures. Opting for an experienced and reputable surgeon can significantly reduce complication rates.
Research on potential surgeons’ backgrounds is vital. Look for those with a history of successful procedures and low complication rates. Experienced surgeons employ meticulous techniques that lower the risk of post-operative infections.
Post-Operative Care
Proper post-operative care is paramount in preventing infections after fat transfer breast augmentation. Patients are advised to strictly follow their surgeon’s instructions regarding wound care and medication use.
Some general tips include:
-
Keeping the surgical area clean.
-
Avoiding unnecessary pressure or trauma to the augmented breasts.
-
Regularly changing dressings as advised by your surgeon.
Understanding Fat Reabsorption in Breast Augmentation
Normal Reabsorption
Fat reabsorption is a natural process after fat transfer grafting. It’s expected that not all transferred fat survives. This is normal.
During the first few months, some of the fat cells are lost. The body naturally absorbs them. This can affect the initial volume achieved right after surgery.
Volume Retention
Long-term, about 60% to 80% of transferred fat remains stable. This means patients can expect a significant portion of the volume to stay.
However, achieving desired results often requires planning for more than one session. Each session adds volume and accounts for any loss from reabsorption.
Multiple sessions help reach the final goal gradually but effectively.
Analyzing the Safety of Fat Grafting in Breast Augmentation
Long-Term Studies
Studies on long-term safety and satisfaction rates are crucial. They offer insights into how patients fare years after surgery. Research shows high satisfaction among those who choose fat grafting.
Most studies report a positive outcome for patients undergoing autologous fat grafting. This is encouraging news for anyone considering this method over traditional implants.
Complication Rates
Comparing complication rates between fat transfer and implants reveals interesting facts. Fat grafting tends to have fewer complications, such as infection or capsular contracture. This is likely due to the use of the patient’s own tissue.
A key advantage of fat transfer is its lower risk profile compared to silicone or saline implants. Patients experience less discomfort and shorter recovery times.
Technique Advancements
Advancements in technique have significantly improved safety outcomes in fat grafting procedures. Surgeons now use more precise methods for harvesting and transferring fat, reducing risks.
The introduction of enriched vascular fraction has further enhanced success rates, making it a safer option for breast augmentation.
-
Improved precision
-
Lower risk of complications
-
Enhanced success with vascular fraction enrichment
Fat transfer grafting has evolved into a good way for breast enhancement, thanks to these advancements in medical techniques.
Closing Thoughts
Fat transfer breast augmentation represents a significant advancement in cosmetic surgery, offering a natural alternative to traditional implants. This technique, which leverages the patient’s own fat to enhance breast volume, underscores the importance of understanding both the potential benefits and the associated risks. From evaluating suitability and analyzing safety concerns to considering the likelihood of fat reabsorption, patients are encouraged to thoroughly research and consult with experienced surgeons. This careful consideration ensures informed decisions that align with individual health profiles and aesthetic goals. As the medical community continues to innovate and refine fat grafting procedures, it is crucial for both patients and practitioners to stay abreast of the latest developments in breast augmentation techniques.
For those considering this procedure, seeking advice from a board-certified plastic surgeon can provide clarity and confidence in your journey towards achieving desired aesthetic outcomes. Let your decision be guided by professional insight and comprehensive understanding.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Fat Transfer Breast Augmentation?
Fat transfer breast augmentation involves transferring fat from other parts of the body to the breasts to enhance their size and shape, offering a more natural alternative to implants.
How does Fat Transfer Breast Augmentation differ from traditional methods?
Unlike implant-based augmentations, fat transfer uses the patient’s own fat cells for a more natural look and feel, reducing the risk of rejection or allergic reactions.
Who is suitable for Fat Transfer Breast Augmentation?
Candidates are those desiring modest breast volume increase, with sufficient donor fat areas. Overall health and realistic expectations are crucial for suitability.
What are the risks associated with Fat Transfer to Breasts?
Risks include fat necrosis, infection, or uneven absorption leading to asymmetry. However, choosing an experienced surgeon minimizes these risks significantly.
How common is Fat Necrosis in Breast Augmentation through Fat Grafting?
Fat necrosis occurs infrequently but can happen when transferred fat cells fail to establish a blood supply and die. The incidence rate varies but remains relatively low with skilled surgical techniques.
Is there a risk of infection with Fat Transfer Breast Augmentation?
As with any surgical procedure, there’s a slight risk of infection. However, adherence to sterile techniques and proper post-operative care significantly reduce this risk.
Can transferred fat be reabsorbed after Breast Augmentation?
Some degree of initial reabsorption is expected as not all transferred fat cells survive. Surgeons often overfill anticipating this loss; however, most results stabilize several months post-procedure.
How safe is Fat Grafting in Breast Augmentation overall?
When performed by qualified surgeons under appropriate conditions, fat grafting in breast augmentation has proven safe and effective with high satisfaction rates among patients seeking subtle enhancements without implants.